What is ODBC – Open Database Connectivity

What is Open Database Connectivity?
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is an open standard Application Programming Interface (API) for accessing a database. In 1992, Microsoft partners with Simba to build the world’s first ODBC driver; SIMBA.DLL, and standards-based data access was born. By using ODBC statements in a program, you can access files in a number of different common databases. In addition to the ODBC software, a separate module or driver is needed for each database to be accessed.
ODBC acts as a bridge between an application and a database. By using ODBC statements, a program can connect to a wide range of databases like SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, and even flat file databases, enabling developers to write database-agnostic code. In practical terms, ODBC decouples the client application from the specific database being accessed, promoting versatility and making it easier to integrate different systems.
ODBC requires a separate driver for each database type. Each driver is responsible for translating ODBC requests into commands that the database understands. The different types of ODBC drivers determine how these connections are established and maintained.
ODBC Specification
The latest version of ODBC specification is available from Microsoft‘s website.
For your convenience, you can also download a PDF version of the current ODBC 3.8 Specification.
ODBC History
Microsoft introduced the ODBC standard in 1992. ODBC was a standard designed to unify access to SQL databases. Following the success of ODBC, Microsoft introduced OLE DB which was to be a broader data access standard. OLE DB was a data access standard that went beyond just SQL databases and extended to any data source that could deliver data in tabular format. Microsoft’s plan was that OLE DB would supplant ODBC as the most common data access standard. More recently, Microsoft introduced the ADO data access standard. ADO was supposed to go further than OLE DB, in that ADO was more object oriented.
However, even with Microsoft’s very significant attempts to replace the ODBC standard with what were felt to be “better” alternatives, ODBC has continued to be the de facto data access standard for SQL data sources. In fact, today the ODBC standard is more common than OLE DB and ADO because ODBC is widely supported (including support from Oracle and IBM) and is a cross platform data access standard. Today, the most common data access standards for SQL data sources continue to be ODBC and JDBC, and it is very likely that standards like OLE DB and ADO will fade away over time.
ODBC Overview
ODBC has become the de-facto standard for standards-based data access in both relational and non-relational database management systems (DBMS). Simba worked closely with Microsoft to co-develop the ODBC standard back in the early 90’s. The ODBC standard enables maximum interoperability thereby enabling application developers to write a single application to access data sources from different vendors. ODBC is based on the Call-Level Interface (CLI) specifications from Open Group and ISO/IEC for database APIs and uses Structured Query Language (SQL) as its database access language.
ODBC Architecture
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) Architecture is a framework that provides a standardized way for applications to access various database management systems (DBMS) without requiring specific database drivers. It serves as an intermediary layer, ensuring that applications can interact with different databases through a common set of APIs, regardless of the database’s underlying structure or language. This flexibility makes ODBC an essential tool for developers looking to integrate diverse data sources seamlessly.
The architecture consists of three key components: the application, the ODBC driver manager, and the ODBC driver itself. The application initiates the communication by sending SQL requests, which are then directed to the ODBC driver manager. The driver manager acts as a dispatcher, determining the correct driver needed for the target database. Drivers play a key role in ODBC architecture by translating requests between applications and databases.
The architecture of ODBC-based data connectivity is as follows:
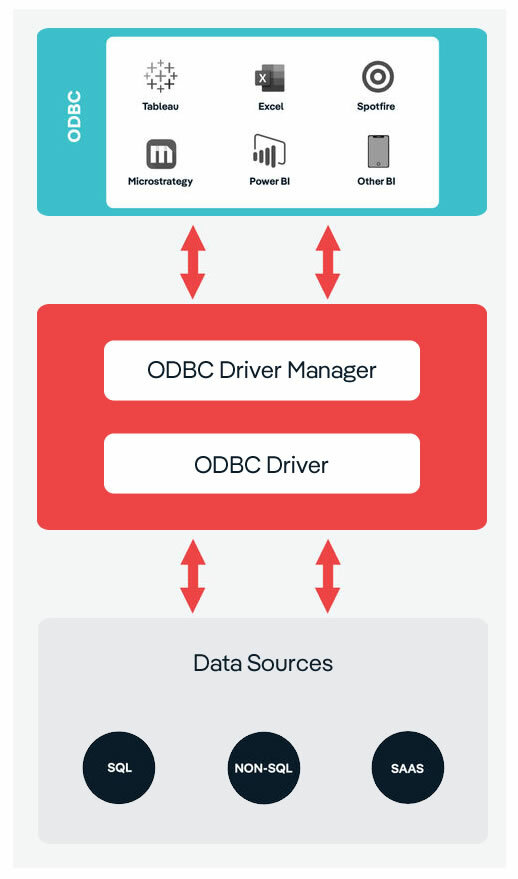
ODBC Enabled Application
An ODBC enabled application is any software that can connect to databases using the ODBC standard. Examples include Microsoft Excel, Tableau, Crystal Reports, and Microsoft Power BI. These applications use ODBC to communicate with databases, allowing them to retrieve, analyze, and manipulate data.
The process involves the application sending SQL commands to the ODBC Driver Manager, which then routes those commands to the appropriate driver for the database in use. Once the database processes the commands, the results are passed back to the application through the ODBC Driver Manager. This enables easy data access without the application needing to handle the details of each database.
ODBC Driver Manager
The ODBC Driver Manager loads and unloads ODBC drivers on behalf of an application. The Windows platform comes with a default Driver Manager, while non-windows platforms have the choice to use an open source ODBC Driver Manager like unixODBC and iODBC. The ODBC Driver Manager processes ODBC function calls, or passes them to an ODBC driver and resolves ODBC version conflicts.
Data Source
A data source is simply the source of the data. It can be a file, a particular database on a DBMS, or even a live data feed. The data might be located on the same computer as the program, or on another computer somewhere on a network.